Steam Condenser is a mechanical device that converts the low-pressure exhaust steam from the turbine into water. Or in other words, it is a device that is used to condense exhaust steam of the turbine into water. It does so with the help of cooling water circulated into it from the cooling tower. It works to achieve two main objectives
1. To maintain low pressure (below atmospheric pressure) at the outlet of the steam turbine so as to obtain the maximum possible energy.
2. To supply pure feed water to the hot well and from hot well the water is again pumped to the boiler with the help of boiler feed pump.
Requirements of Steam Condensing Plant
The principle requirements of the steam condensing plant are:
1. Condenser:
It is a closed vessel used to condense the steam. The low-pressure steam gives off its heat to the coolant (here water from the cooling tower) and gets converted into the water during the process of condensation.
2. Condensate Extraction Pump:
It is a pump which is installed in between the condenser and hot well. It transfers the condensate from the condenser to the hot well.
3. Hot Well:
It is a sump that lies in between the condenser and the boiler. It receives the condensate from the condenser by condensate pump. The feed water is transferred from the hot well to the boiler.
4. Boiler Feed Pump:
It is a pump installed in between the hot well and boiler. It pumps the feed water from the hot well to the boiler. And this is done by increasing the pressure of condensate above boiler pressure.
5. Air Extraction Pump:
It is a pump used to extracts or removes the air from the steam condenser.
6. Cooling Tower:
It is a tower that contains the cold water and this water is made to circulate within the condenser for cooling of steam.
7. Cooling Water Pump:
It is a pump lies in between the cooling tower and condenser. It circulates the cooling water through the condenser.
Working of Steam Condenser
The steam condenser receives the exhaust steam from one end and comes in contact with the cooling water circulated within it form the cooling tower. As the low-pressure steam comes in contact with the cooling water, it condenses and converts into water. It is connected to the air extraction pump and condensate extraction pump. After the condensation of steam, the condensate is pumped to the hot well with the help of condensate extraction pump. The air extraction pump extracts the air from the condenser and creates the vacuum inside it. The vacuum created helps in the circulation of cooling water and flow of condensate downward.
Also Read:
- What are Different Types of Turbine?
- What is Gas Turbine Power Plant?
- Steam Power Plant Construction,Working, Advantages and Disadvantages with Diagram
Classification of Steam Condenser
The steam condenser is classified as
1. Jet condensers or mixing type condenser
2. Surface condenser or non-mixing type condenser
Jet Condenser
Jet condenser is a condenser in which the condensate gets mixed with the cooling water. That’s why it is also called as mixing type condenser.
This type of condenser is used sometime because it lost some of the condensate and requires high power for the pump during the process of condensation.
In jet condenser, as the condensate is not free from the salt, so it cannot be used as feed water for the boiler. It can be used at the place where sufficient amount of good quality water is available.
Types of Jet Condenser
(i) Parallel Flow Jet Condenser
In parallel flow jet condenser, the steam and water enters into the condenser at the top and leaves at the bottom.
The cooling water and steam enters at the top. As both steam and cooling water mix with each other, the steam gets condense. The condensate, cooling water and air moves downward and it is removed by two separate pumps known as air extraction pump and condensate extraction pump. The condensate pump transfers the condensate to the hot well and from there the extra water is made to flow in cooling water tank or pond through overflow pipe.
(ii) Counter Flow or Low Level Jet Condenser
In counter Flow or low level jet condensers, the steam enters at the bottom and the cooling water at the top. The steam flows upward and meets the cooling water coming downward.
In these types of steam Condensers, the air pump is located at the top. Air pump creates vacuum and this vacuum draws water from the cooling tower. The cooling water enter into the condenser and falls on the perforated conical plate. The perforated conical plates convert the cooling water into a large number of jets as shown in the figure. The falling jet of water caught in the trays and from there it escapes out in second series of jets and meets the exhaust steam entering at the bottom. As the steam mix with the water, it gets condense. The condensate and cooling water moves down through a vertical pipe to the condensate pump. And finally the pump delivers it to the hot well.
(iii) Barometric or High Level Jet Condenser
Barometric or high level jet condensers are provided at high level with a long vertical discharge tube or tailpipe. It does not have condensate extraction pump and the condensate and cooling water flows in the hot well because of the gravity. An injector pump is used to flow cooling water at the top of the condenser.
These types of jet condensers are used at a high level with a vertical discharge pipe. In this condenser, the steam enters at the bottom and flows in upward direction and meets with the down coming cooling water. Its working is similar as the low level jet condenser. The vacuum is created at the top of the condenser shell. With the help of vacuum and injector pump, the cooling water is moved to the top of the condenser. The condensate and cooling water comes down in the hot well through a long vertical discharge pipe. And finally the extra hot water flows to the cooling tank or cooling pond by an overflow pipe
(iv) Ejector Condenser
In ejector condensers, it has a non-return valve through which exhaust steam enters, hollow truncated cones, and diverging cone.
In these condensers, the cooling water is injected at the top. The steam enters into the condenser through a non-return valve. The steam and water mixes with each other while passing through series of hollow truncated metal cones and steam changes into water. At the end of the metal cones a diverging cone is present. When the condensate passes through diverging cone, its kinetic energy is partly transformed into pressure energy.
The condensate and cooling water is then discharged to the hot well.
Also Read:
- What is Combined Cycle Power Plant? – Complete Explanation
- How Hydropower Plant Works? – Complete Explanation
- How Geothermal Power Plant Works – Explained?
Surface Condensers
Surface condenser is a type of steam condenser in which the steam and cooling water do not mix with each other. And because of this, the whole condensate can be used as boiler feed water. It is also called as non-mixing types condenser.
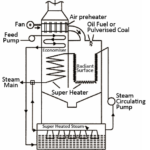
The figure above shows the longitudinal section of a two pass surface condenser. It consists of a horizontal cylindrical vessel made of cast iron and packed with tubes. The cooling water flows through these tubes. The ends of the condensers are cut off by the perforated type plates. The tubes are fixed into these perforated type plates. It is fixed in such a manner that any leakage of water into the center of condensing space is prevented. The water tubes are passed horizontally through the main condensing space. The exhaust steam from the turbine or engine enters at the top and forced to move downward due to the suction of the air extraction pump. In this steam condenser, the cooling water enters into boiler through lower half of the tubes in one direction and returns in opposite direction through the upper half as shown in the figure above.
This type of condenser is used in ships as it can carry only a limited quantity of water for the boiler. It is also widely used for the land installation where there is a scarcity of good quality of water.
Types of Surface Condensers
The surface condenser on the basis of direction of flow of condensate, the arrangement of the tubing system and the position of the extraction pump are classified as
(i) Down Flow
In Down flow surface condenser, the steam enters at the top of the condenser and flows downwards over the tubes due to the gravity and air extraction pumps. The condensate gets collected at the bottom and then pumped with the help of condensate extraction pump. The pipe of dry air extraction pump is provided near the bottom and it is covered by baffle plates so as to prevent the entry of the condensate into it.
The steam in down flow condenser flows perpendicular to the direction of flow of cooling water, so it is also called as cross-surface condenser.
(ii) Central Flow
In central flow condenser, the steam enters at the top of the condenser and flows in downward direction. In this the suction pipe of the air extraction pump is provided in the center of the tube nest as shown in the figure. Due to this placement of the suction pipe in the center of the tube nest, the exhaust steam flows radially inward over the tubes towards the suction pipe. The condensate is collected at the bottom of the condenser and pumped to the hot well.
We can say that it is the improved form of the down flow surface condenser.
(iii) Regenerative
In regenerative surface condensers, the condensate is heated by the use of regenerative method. In that the condensate is passed through the exhaust steam coming out from the turbine or engine. This raises its temperature and it is used as the feed water for the boiler.
(iv) Evaporative
In evaporative surface condensers, the steam enters at the top of the condenser in a series of pipes over which a film of cold water is falling. At the same time, current of air is made to circulate over the film of water. As the air circulates over the water film, it evaporates some of the cooling water. As a result of this rapid evaporation, the steam circulating inside the series of pipes gets condensed. Remaining cooling water that left is collected at an increased temperature and reused. It is brought to the original temperature by adding required quantity of cold water.
Advantages of Steam Condenser
- It increases the efficiency of the plant.
- It reduces the back pressure of the steam and as a result of this, more work can be done.
- It reduces the temperature of the exhaust steam and this allows to obtain more work.
- It allows the reuse of condensate for the feed water and hence reduces the cost of power generation.
- The temperature of the condensate is more than the feed water. This reduces the supply of heat per kg of steam.
Comparison of Jet and Surface Condenser in Tabular Form
S.no | Jet Condenser | Surface Condenser |
| 1. | Exhaust steam and cooling water mixed with each other. | Exhaust steam and cooling water are not mixed with each other. |
| 2. | It is less suitable for high capacity plants. | It is more suitable for high capacity plants. |
| 3. | The condensing plant using this type of steam condenser is simple and economical. | The condensing plant using surface condenser is costly and complicated. |
| 4. | Condensate is wasted and cannot be reused. | The condensate is reused. |
| 5. | Less quantity of circulating water is required. | A large quantity of circulating water is required. |
| 6. | It has low maintenance cost. | It has a high maintenance cost. |
| 7. | In the jet condenser, more power is required for the air pump. | In the surface condensers, less power is required for the air pump. |
| 8. | High power is required for water pumping. | Less power is required for water pumping. |













mechanicalbooster.com is the best platform to study and this platform provides information in a simple language. Very very thank you for providing like information.