What is Benson Boiler?
Benson Boiler is a high pressure, drumless, supercritical, water tube steam boiler with forced circulation. This boiler was invented in the year 1922 by Mark Benson. This boiler is a supercritical boiler in which the feed water is compressed to a supercritical pressure and this prevents the formation of bubbles in the water tube surface. The bubbles do not form because at supercritical pressure the density of water and steam becomes the same. It was Mark Benson who first proposed the idea to compress the water at supercritical pressure before heating into the boiler and due to this the latent heat of water reduces to zero. As the latent heat of water reduces to zero the water directly changes into steam without the formation of bubbles.
Construction or Main Parts
The main parts of Benson boiler are:
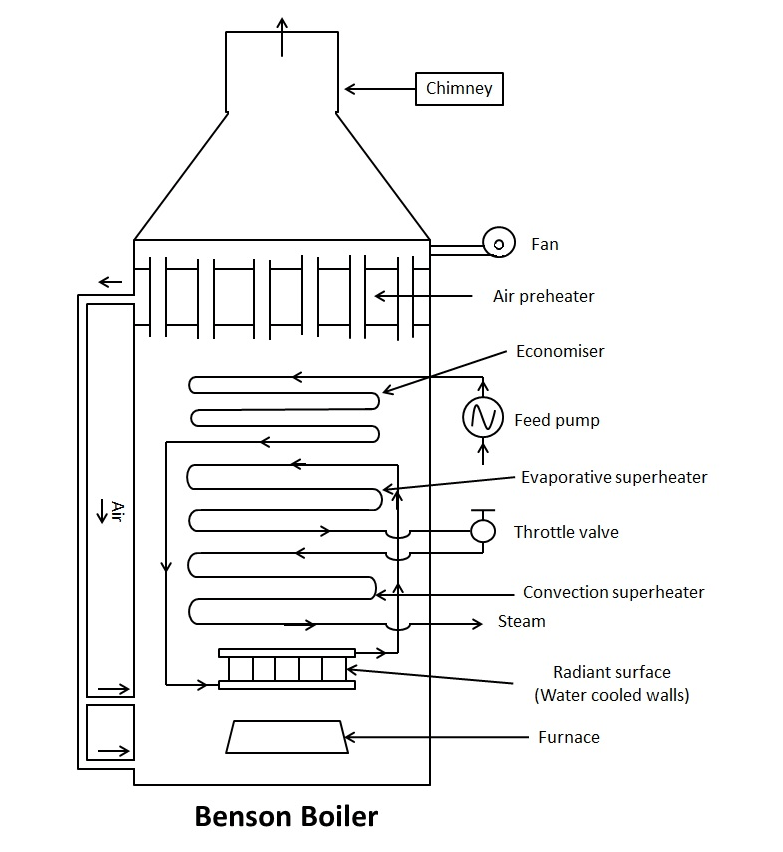
1. Air Preheater
It preheats the air before entering into the furnace. The preheated air increases the burning efficiency of the fuel.
2. Economiser
It heats the water to a certain temperature.
3. Radiant Superheater
It is superheater that heats the water with radiation produced by the burnt fuel. It raises the temperature to supercritical temperature.
4. Convection Evaporator
It evaporates the superheated water and converts them into steam. It does so by the convection mode of heat transfer to the water from the hot flue gases.
5. Convection Superheater
It superheats the steam to the desired temperature (nearly 650 degree Celsius).
6. Furnace
It is the place where the fuel is burnt.
7. Feed Pump
It is used to supply the water inside the boiler at supercritical pressure of 225 bars.
Also Read:
- What is Cochran Boiler?
- What is Babcock and Wilcox Boiler?
- Lancashire Boiler Construction, Working with Diagram
Working Principle
It works on the principle that the pressure of the water is increased to the supercritical pressure (i.e. above the critical pressure of 225 bar). When the pressure of water is increased to the supercritical level, the latent heat of water becomes Zero and due to this, it directly changes into steam without boiling. And this prevents the formation of bubbles at the tube surface.
Working of Benson Boiler
- In Benson Boiler, the feed pump increases the pressure of the water to the supercritical pressure, and then it enters into the economiser.
- From economiser, the water passes to the radiant heater. Here the water receives the heat through radiation and partly gets converted into steam. The temperature raises almost to the supercritical temperature.
- After that mixture of steam and water enters into convective evaporator where it is completely converted into steam and may superheated to some degree. Finally it is passed through the superheater to obtained the desired superheated steam.
- This superheated steam is then used by turbines or engines to produce electricity.
Advantages
The various advantages of the boiler are
- It is a drumless boiler and hence the weight of this type of boiler is 20 % less as compared with other types of boiler.
- It is light in weight.
- Occupy smaller floor area for its erection.
- Explosion hazard is almost negligible because of the use of smaller diameter tubes.
- It can be started very easily within 15 minutes.
- It avoids bubble formation due to the supercritical pressure of water.
- Transportation is easy.
- This boiler may achieve thermal efficiency upto 90 %.
Application
This supercritical boiler is used in different industries to generate steam for the production of electricity or mechanical power. The average operating pressure, temperature and capacity of benson boiler is 650 degree Celsius, 250 bar and 135 tonnes/h.
Conclusion
Here, We have studied about what is Benson boiler, its main parts, working, advantages with applications. I hope you easily grasp the topic. If you find this pieces of information valuable and useful then don’t forget to like and share it.








Good explanation …..