Introduction
On May 30th2020, the world witnessed a flawless launch of ‘Crew Dragon’, a capsule designed to take astronauts back and forth to International Space Station. This commercial spacecraft is a joint venture of NASA and Space X – a first of a kind- and boosted of advanced technology in the field of mechanical and aerospace engineering. It not only looked beautiful but was also incorporated and endowed with a plethora of modern technologies. The spacecraft was quite reminiscent of those we see in a sci-fi movie being packed with advanced engineering technologies such as 3D printed helmets, 3D printed Super Draco Engine, touch screen display, and automatic docking system. All this will certainly going to empower and inspire generations for many coming years.
So let us take a step back and see a bird’s eye view of this core engineering, the oldest and broadest discipline, which integrate mathematics and engineering physics principles with material sciences in order to design, analyze, manufacture, and ultimately controlling the working model.
What is Mechanical Engineering?

The mechanical engineering required an understanding of other basic fundamentals of Chemistry, Physics, Civil Engineering, Electrical Engineering, and Aerospace Engineering, Automobile Engineering to design, develop, and operate any machinery.
It is a field of a core concept of mechanics, dynamics, and material science, strength of materials, thermodynamics, structural analysis and electrical energy along with tools like Computer-Aided Design (CAD), Computer Aided Manufacturing (CAM). Also, the usage is vast from analyzing vehicle design and performance to its applicability in other sectors like aircraft, ships, robotics, nuclear power plants, transportation and many more. Moreover, mechanical engineers are pursuing careers in composites, nanotechnology, and especially in Mechatronics.
According to latest NASSCOM EY report, with coming of Artificial Intelligence many jobs profile are going to be replaced such as Design Engineer to Interaction designer, Operation Excellence Manager to Continuous Improvement Manager, Mechanical to Mechatronics Control Engineer, Clay Modeler to 3D Clay Modeler, Customer Care Executive to Customer Care Expert. In short, it is a foregone conclusion that we need to advance and recalibrate our skill set.
History of Mechanical Engineering
Though mechanical engineering was introduced as a separate engineering field in the early 19th century, but there were many applications and instances of its from time immemorial. This world has produced many Lukeman in ancient and medieval times who have transformed the world through their inventions. If we talk about the simple machines which were defined by the renaissance scientist (European scientist from 14th to 17th century) which changes direction and magnitude of forces by simply multiplying the force.
6 Simple Machines
1. Wedge –

This was used in the Stone Age when the humans used to break blocks of stones through a hand axe. This hand axe was the first and foremost example of the wedge. Its function is to transfer the force from its blunt edge of its inclined surface. The wedge merely transforms energy and collects it to the sharpen point. The mechanical advantage is given by the ratio of the length of its slope to the width( M.A= Length/width)
2. Inclined planes –
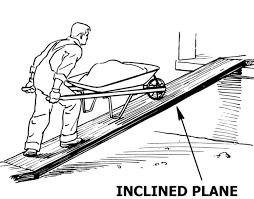
It existed for thousands of years, also known as ramps, in many natural ways like mountains and slopes. This is a passive static device that is skewed at an angle with one at the high end and other at lower to lift heavier objects. It is easier to slope an object rather than lifting it vertically. As far as we move away from the vertical imaginary line the force required to lift the object on the inclined plane reduces. There was always a bone of contention between many Greek scientists on the consideration and classification of inclined planes in the simple machines which were later on sorted out by renaissance scientists.
3. Wheel –

One of the earliest applications of the wheel was found in Potter’s wheel which was used to fabricate clay pots, also known as slow wheels. This was famous in the Middle East in about 5th millennium BCE
The Ljubljana marshes wheel, the first wooden wheel with an axle, dating back to around 5,150 years back was discovered in the city of Ljubljana of Slovenia in 2002. This was one of the oldest and ancient wooden wheels which was made of ash and oak. Wheels and axles are attached together in such a way that the force is transmitted from one to another.
Also Read:
- What is Slotter Machine?
- What is Lathe Machine? Main parts, Operations and Working
- What is Milling Machine – Operation, Parts and Types.
4. Lever-
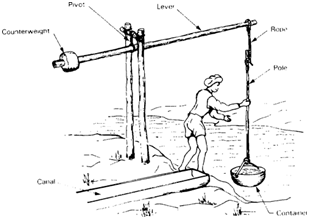
First crane machine, in the early 3000BC, was invented somewhere in Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq) known as Shadoof or Shaduf to lift water from canals or to move heavy objects from the extended lever end which is pivoted at a fasten hinge. The lever amplifies the input force to a greater output force at another end known as mechanical advantage, which has many applications in various fields from a simple bottle opener to the braking system.
5. Pulley –

The most primitive evidence of the pulley dated back to 2nd millennium BC, somewhere in Mesopotamia and ancient Egypt. The hero of Alexandria, who invented Aeolipile(which we will discuss later), is also identified as a 6 simple machine which provides mechanical advantage and was used to lift heavy machines using a combination of block and tackle. A pulley is designed to transfer power between the shaft and cable.
6. Screw-
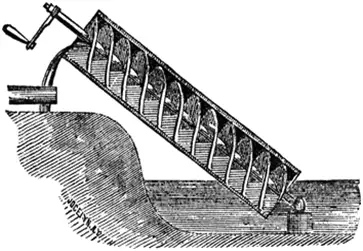
A screw is a tool which doesn’t necessarily have a thread or shaft like a modern days screw. This was one of the last invented simple machines which firstly appeared in the Neo-Assyrian period (Iron Age between 911-609BC) in East Asia of Mesopotamia and later appeared in ancient Egypt and ancient Greece. It was used as a screw pump or water screw, in ancient Egypt before the advent of Archimedes screw, to lift water from the lower end to high end by converting torque into linear force or transforming rotational motion into linear motion.
Contribution of some Lukeman Engineers
Greatest minds have walked on this planet since time immemorial. Many inventions have took place in different parts of the world. The first ever practical and earliest water mills were invented somewhere in Persia, modern day Iraq and Iran, in early 4th century BC. These mills use water as a source to transform energy from one wheel to another and were used to grind flour, needed for the production of many other materials like paper, textiles, timber and many metal products for many years.
Then in between 10-70AD first steam powered machine, known as Aeolipile, was developed. It was the precursor to further refined steam engine of the Industrial Revolution era. Zheng Heng from china invented seismometer and improved the water clock around 78-139AD. Ma Jun, a Chinese Engineer (200-265 AD) – invented chariot with differential gears. Su song (1020-1101AD), another Chinese engineer, invented an endless power transmitting chain drive.
Likewise, there were also many inventions during the Islamic golden age between 7th to 14th century AD.
Al-Jazari, born in Mesopotamia, created the basics of mechanism in today’s world: crankshaft and camshaft in 1206.
Involvement of Sir Isaac Newton took mechanical engineering to another level during the 17thcentury. That was visible through the application of Newton’s laws of motions and calculus (the mathematical basis of physics).
Early 19th century industrial revolution when Commerce, necessity, raw material, and the invention came together to kick start the Industrial Revolution allowed mechanical engineering to emerge as a separate field. Then in 1847 the first British professional Society of Mechanical Engineers was established and finally in 1880, American society of mechanical engineers (ASME) was established
The invention of steam Engine
The forgotten Hero – Herons of Alexandria
To credit a single person for inventing steam engine would be an injustice. From ages, many have worked through hundreds and thousands of year for a steam engine to take its final shape.
Steam Engine was one invention that could have revolutionized the world. It all started back in the 1st century AD, when Heron of Alexandria, an ancient Egyptian, firstly invented the working model of Aeolipile also known as Hero’s Engine. This strange machine (as depicted in fig) is Herons Steam Ball, the first steam turbine machine and the fastest revolving mechanical instrument of the ancient world. Heron’s was just a half a step away from inventing the steam engine. He knew the principle of steam power and had designed a revolutionary device which was a sight to behold. Herons had managed to control the power of steam, and it was a remarkable breakthrough.
This device could have started the Industrial Revolution 2,000 years ago, but sadly it could not. Nevertheless, Herons gave a glance of forthcoming possibilities to the world.
But the question arises that why Herons greatest invention could not start the revolution. Think about the possibilities.

After that Thomas Savery, a British inventor invented first steam machine in 1698 that did some useful work to pump out water from the coal mines. It used an ample amount of coal to remove small quantity of water. Then later on in 1712 Thomas Newcomen, another British inventor, improvised on Savery’s inefficient steam pump by practically moving the piston in one direction by using steam. However, both Savery and Newcomen were not aware that this amazing machine could have changed the world in later half of 17th and early 18th Century.
Then in 1736, James Watt, a Scot who was very much product of the 18th century -the first century of modernity- was born. He benefited from the Scottish Enlightenment that was developing intellectually, economically, and culturally. He essentially believed in the power of knowledge, the power of ideas to bring about an immediate change in the here and now world. He’s sometimes depicted quite wrongly as being the inventor of the steam engine, as we have seen many of the above mentioned engineers contributed to its development. He is credited for perfecting steam power technology to make it more efficient and ultimately more portable.
Why Mechanical Engineering is the mother of all engineering?
As we must have heard from our father and forefather that Mechanical engineering is the Evergreen field. Yes, that’s true because it’s the base for many other engineering fields (as discussed below).There is barely a field that is apart and oblivion from this field. From medicine, automobile, construction, electrical, to IT industry, every field has some mechanical applications.
Let’s have a look.
Branches of Mechanical Engineering
Because mechanical engineering is the mother of all engineering, there are many engineering expertise that fit within its scope. So, here are the most common branches where graduating students can find their careers.
1. Acoustical Engineering
Started in the late 1920s, this specialization deals with the study of sounds, vibrations, and frequency. Every matter in this world has its own set of frequencies and vibrations. One major role of an acoustical engineer is to reduce noise pollution or noise control because unwanted noise has an adverse impact on animals and humans. It is not just about reducing unwanted noise; it covers fields of the medical for ultrasound, whether they are creating concert halls, cinema halls, and clear ultrasonic scans.
Incorporated in every aspect of modern society, from automobile design to aerospace design, it is vividly used to control sound and vibrations.
2. Aerospace Engineering

It is the product of various engineering disciplines and technology which includes aerodynamics, propulsion, materials science, avionics (Deals with the electronic side of aerospace eng.), structural analysis and design, and manufacturing. This field is concerned with the design and development of aircraft and spacecraft. It has 2 major and interlinked branches- Aeronautical and Astronautical Engineering. It has various applications in military, space exploration.
3. Automotive Engineering

This field focuses on the design, dynamics, and development of all types of road vehicles. Modification of vehicles is also part of this vast field. It starts with the design of the vehicle using various tools like Solidworks, CATIA, and Ansys, in parallel with the dynamics of the vehicle which later on shift into the production plant for manufacturing of the desired vehicle. It includes the study of various fields apart from mechanical such as electronic, safety elements, software. It’s a research intensive domain where there is direct use of mathematics and physics. It’s comprised of three major functions: Production, Development, and Manufacturing. The society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) is the complete source for this field.
Also Read:
- What are the Melting Points of Metals?
- What is Cast Iron? Complete Explanation
- Solar Power Plant – Main Components, Working, Advantages and Disadvantages
4. Marine Engineering

Do you know the first Marine Engineer? Yes, none other than Archimedes who had designed and developed numerous of a marine engineering systems in his era. Thomas Newcomen, as we discussed above who developed the steam power machine to take out water from mines is also the exemplar of this field. This field concern with the design, dynamics development, repairing, and maintenance of all types of overseas vessels and crafts. It also includes oceanographic engineering, offshore engineering which deals with the biological and physical aspects of the ocean and design and structural analysis of offshore wind farms and oil platforms. The society for Naval Architects and marine engineers (SNAME) is the complete source for this field.
5. Mechatronics Engineering

At first Mechatronics Engineering is the amalgamation of two fields which is Mechanical and Electronics. As later on this field advances with time, the definition is broadened to involve many more technical areas such as robotics, telecommunication, coding, etc. Tetsuro Mori, a Japanese engineer, created or you can say coined the term “Mechatronics” in 1969. The industrial robots are the prime paradigm of this field.
6. Railway Engineering

It all started with the advent of the railways in the early 19th century, during industrial revolution, when the need arouses for the group of engineers who can design, develop and every possibility associated with Railway Engineering. It includes design, construction, and maintenance of tracks for safe and efficient engagements with rails.
Different areas to study and explore in the Mechanical Engineering Field
Mechanical Engineers have a broad range of areas of interest when it comes to jobs in different sector of the industries. It is one of the most extensively used form of engineering ranging anywhere from medicals to rockets. If you are in initial days of college it’s important to understand your strength before choosing any area which obviously require immense research work too.
1. Aerodynamics and Fluid mechanics
Aerodynamics
It is study of how gases interact with moving objects. It’s chiefly concerned with the forces of drag and lift, which mainly caused by air moving over and around the solid bodies. Engineers applied the principle of aerodynamics to several things like during vehicle design or aircraft design, etc. it’s a sub field of fluid dynamics.
Fluid mechanics
It is a sub discipline of continuum mechanics, the study of physics of continuous materials, is a branch of physics concerned with the mechanics of fluids (Liquid, gases) which deform its shape when subjected to a force. It can be sub categorized in fluid static and fluid dynamics. The former represent study of fluid in rest, and later represent study of fluid in motion. It’s basically a mathematical approach used to address by numerical method using computers such as Computational fluid dynamics (CFD).
It has application in many fields such as Aerospace, Biomechanics, Metrology, Automobile, and many more.
2. Combustion, Energy and Environment
Mechanical engineers are widely involved in designing of the internal combustion engine, gas turbine, propulsion etc. this area are designed for those who would like to work in the field that uses combustion to increase the efficiency and to minimize the pollution. In many universities, researches are going on alternate use of liquid fuels for aircrafts and automotives; Super- adiabatic combustion; combustion of solid particles with water for hydrogen production etc.
3. Mechanical design
This is what when an idea comes into reality, starts from collecting requirements then creating a conceptual idea and creating the comprehensive design at the end. It involves designing of parts, components, products of various mechanical systems. For example -designing of shaft, gears, bearing, and various fasteners falls into the scope of mechanical designing. While designing one needs to think about various parameters such as weight, size, manufacturability, factor of safety (FOS), reliability etc. in general, a mechanical design should be evaluated with clear and complete statements of – Functions, specifications, and evaluation criteria. There are several tools used to design various products such as AutoCAD, SOLIDWORKS, CATIA, Inventor, Fusion 360 etc.
4. Manufacturing
It is a very broad area of interest which constantly changing as technology regularly evolving and developing. These are the steps which are used to convert a raw material into a value added product. The first step of manufacturing is product design (as we discussed above) and specification from which a market ready product is made. A major activity of a mechanical engineer is to study various production methods and techniques.
There are many methods of manufacturing such as Mass manufacturing, Lean manufacturing, Rapid manufacturing, Just –in- time manufacturing, Agile manufacturing, Flexible manufacturing and many more.
5. Material science
This field helps to understand how the material influences its structure, and thus the material properties and characteristics. Behind any product design there is a complete study and analysis of all the material being used. Materials are generally chosen based on their performance in the provided application and sometimes also tailored made to fit a specific product requirement. The understanding of processing-structure-properties associations is known as the material paradigm. This is used in several of areas such as nanotechnology, biomaterials, and metallurgy.
6. Dynamics
It is division of mechanics which deals with the study of forces, and their effects on motion of solid object. To study vehicle performance and efficiency one needs to understand the basic concept of vehicle dynamics. It involves various topics such braking system, suspension, steering, tires and wheel, transmission systems like gearbox, engine, and axles.
Industry 4.0 and its Impact
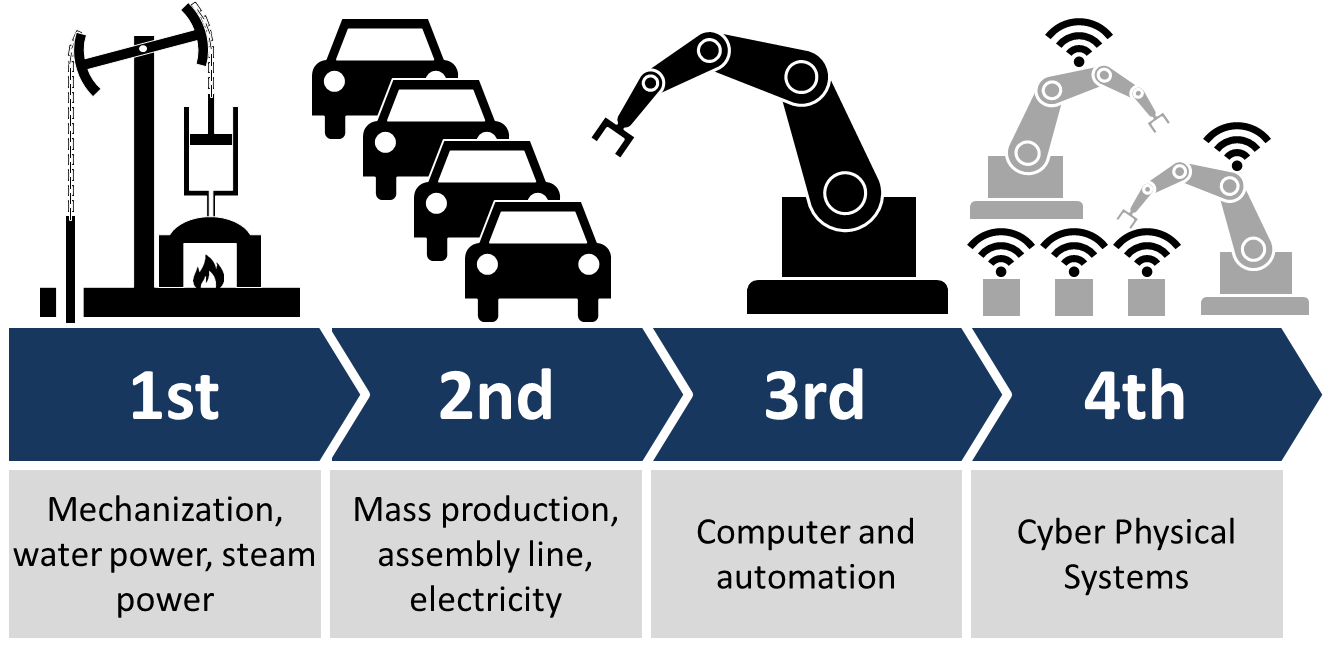
Industry 4.0 is characterized by fusion of technologies which blur the lines between physical, digital and biological spheres. We are entering in a high tech world where machines are not just intelligent but are also brilliant. Industry 4.0 comprises of technologies like Internet of things, Machine learning, Artificial Intelligence, Big data, Additive manufacturing (AM) which is having an unsettling shock on mechanical engineering design and production. It is deeply varying the way we design and manufacture and is making products far more reliable vis-à-vis products manufactured and designed via traditional methods.
As Industry 4.0 grips the market, the engineers will embrace these digital tools and technologies. This will allow them to manufacture high end quality products efficiently through data driven intelligence that will react rapidly to consumer needs and will increase demand of tailored products to match individual preferences which in turn will improve the loyalty of customer. Machines like Engines, Turbines, locomotives and many medical devices are also becoming analytical and predictive, thus communicating with each other and with us intelligently and automatically. This will be helpful in predicting the breakage and thus eliminating many unprecedented errors and faults which will ultimately improve productivity.
Mechanical jobs are impacted by various factors and perimeters. It is stated that there are some inevitable forces like Globalization, Demographic change and adoption of Industry 4.0 happening over a period of next 5 years which will require mechanical engineer to upgrade their skills.
As of 2022, a ball park figure, in automotive and mechanical sector, 5% to 10% of employees will have jobs that do not exist today. 50% to 55% profuse workforce will be in jobs with utter changed skills set. Also 10% to 15% are facing threats on their jobs currently.
Data storage and analysis is becoming a dime a dozen these days, which is radically changing and creating countless jobs profile in nearly every sector: automotive analytics engineer, research analyst, quality analyst etc.
But the questions and the most vital one that remains –
- Is our education system evolved enough to tackle these technological changes and advancement?
- Are our students adequately skilled in this fast-changing world?
The answers to these questions will lay the ground for a new age of mechanical engineering.









