Introduction
“Brakes are as important as an engine for an automobile” very rightly said as if we require an engine to run a vehicle than we also require brakes to stop it, This statement also resembles with the Newton’s first law, we all are familiar with. As we know now a day in light vehicles we use hydraulic brake system to stop or decelerate the vehicle, But the questions arises, Is the hydraulic brake system effective when it comes to heavy vehicles? If not then, What do we need to stop or decelerate the heavy vehicles like buses and trucks? Let’s hunt the answers.
A pneumatic brake or compressed air brake system is the type of brake system in which the compressed liquid fluid from the hydraulic system is replaced with the compressed air for applying pressure to the master cylinder’s piston which in turn presses the brake pads in order to stop or decelerate the vehicle.
Pneumatic air brake system is usually used in heavy vehicles like buses and trucks.
Why do We Need Air Brake System?
As we have already discussed brake system is the need of an automobile vehicle but as we all know when it comes to the application every vehicle is not same as some vehicle are used for light utility purposes like cars and bikes and some are used for heavy purposes like buses and trucks, so there is a need of different braking systems due to the following reasons-
- As the load over light vehicle and heavy vehicle varies the brake force required to stop the heavy vehicle is far more than that of light vehicle, so the heavy vehicles should be equipped with a braking system that can provide the enough brake force that can stop or decelerate the vehicle.
- When we talk about light weight vehicles, hydraulic brakes provides more than enough brake force to stop or decelerate the vehicle due to its short dimension but when it comes to the heavy vehicles which are large in size the effectiveness of hydraulic brake system is a great concern.
- As the fluid is used to press the piston in hydraulic braking system the safety is the great concern as if there is any leak in the components of the hydraulic system the efficiency of the braking is readily reduced or even lost completely, since air is always available so the brake failure due to leakage is the less concern in the air braking system.
- The components (master cylinder, brake lines etc.) size of the hydraulic brake system increases with the increase in the size of the vehicle which in turn makes it very complex to install, which is not a problem with the air brake system.
- Due to safety measures like brake failure and efficiency, Government has made it compulsory for heavy vehicles like buses and trucks to use air brake system.
So due to these above mentioned reasons on March 1872, George Westinghouse introduced an air braking system for the braking system in railways due to its fail-safe feature.
Also Read:
- How Drum Brakes Work?- Easiest Explanation Ever
- How Disc Brake Work? – Best Explanation
- Drum Brakes vs Disc Brakes – Which is Better?
Main Components

1. Air Compressor
It is the compressor that pumps air from atmosphere to the air storage tank and is driven by the engine through belt drive.
2. Air Compressor Governor
It is the governing device used in air brake system that controls the compression pressure of the air that is pumped to the air storage tank through air compressor.
3. Air Dryer
It is the device used to remove moisture content from the air coming from the atmosphere to prevent the lines and air storage from water condensation that can cause brake failure such as during winters due to the freezing of that condensed water.
4. Air Storage (Reservoir)
It is the tank that is used to store the compressed air sent by the compressor, this storage always has enough amount of compressed air so that the brakes can be applied several time and also prevents the brake failure when the air compressor shows malfunctioning.
5. Brake Pedal
It is the mechanism that is operated by the driver and is used to actuate the brakes in order to stop or decelerate the vehicle. Brakes, when pressed, pushed the compressed air which in turn applies brakes to the moving tire.
6. Dirt Collector
It is the device that is placed inside a brake pipeline at place where a branch is separated and taken off to the triple valve which removes dirt from the air before sending it to the triple valve
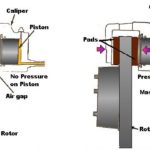
7. Brake Cylinder or Brake Chamber
It is the device that consists of a cylinder and piston over which the compressed air pressure is applied in order to push brake pads which in turn makes frictional contact with the disc or drum in order to stop or decelerate the vehicle.
8. Brake Valve or Triple Valve
The actuation and release of brake require continuous release and building of pressure inside the brake lines and brake cylinder according to the motion of the brake pedal this is done by the triple valve used in the air brake system.
9. Brake Drums
The brake drum is the component through which the brake force due to frictional contact between brake pads and drum lining is transferred to the wheel in order to stop or decelerate the vehicle, Outer surface of the brake drum consisting of drum lining rotates with the wheel and the inner part consisting of brake shoes stays in its state of rest when the brake pedal is not pressed.
Note – Usually brake drums are used in air brake system but with suitable arrangement disc brake can also be used in air brake system.
Also Read:
- Different Types of Engine
- How Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) Works?
- What is Magneto Ignition System and How It Works?
Working of Air Brake System
When the driver of a vehicle presses the brake pedal in order to stop or decelerate the vehicle the following processes takes place-


- When the driver starts the engine the brake compressor starts as it is driven by the engine which in turn starts compressing the atmospheric air and through the compressor governor this compressed air with optimum pressure is sent to the compressed air reservoir which always has some amount of air stored from the previous cycle.
- When the driver presses the brake pedal the outlet valve of the triple valve closes and inlet valve opens up which in turn gives passage to the compressed air from the reservoir to pass through the brake lines of the system.
- This compressed air flowing through the brake lines is then transferred to the brake cylinder which has piston inside it.
- When the compressed air applies pressure over the piston inside the brake chamber, the piston moves away from its original position which converts this pneumatic energy into mechanical energy.
- On the wheel end of the brake cylinder, brake drums are placed inside which there is a housing of the mechanical actuator like springs or slacks having brake pads at its outer end.
- Due to the movement of piston because of the pressure applied by the compressed air, The mechanical actuator inside the brake drum expands which in turn pushes the brake pads in an outward direction in order to make frictional contact with the rotating drum lines.
- With this frictional contact between brake pads and rotating drum lines brakes are applied to the wheels in order to stop or decelerate the vehicle.
For a Better explanation about how the air brake system works watch the video given below:
Application
Due to its property of preventing brake failure air brake systems are widely used in various vehicles but in heavy vehicles like trucks and buses due to the government vehicle regulations, air brake system is mandatory.
- It is used in railways
- All the trucks and busses on the road today use air brake systems, few from them are.
- Volvo 9400PX buses.
- Bharat Benz 3123R truck.
Conclusion
Here we have learnt about what is Air Brake System and how it works. We have also discussed the main components and application. I hope you have understood it clearly and if you found this information useful and valuable then don’t forget to like and share it.






![What are the Components of an Automobile? [Complete Guide] Main components of Automobile](https://mechanicalbooster.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/04/Main-components-of-Automobile-150x150.jpg)