Have you ever imagined that gear ratio can be possible without gears? Interestingly right, what if the system creates countless gear ratios? To create an infinite gear ratio is extraordinary thinking but is it possible? Yes, everything is possible when it is a matter of automobiles. The manual gearbox or traditional transmission system has a fixed number of gears and gear ratios. Metamorphosis of automotive technology is unpredictable and developed two pulley systems of power transmission from the engine to the wheel. Vehicle with continuously variable transmission (CVT) more popular in recent years and Japanese automobile companies are good at using this technology in their vehicles. CVT is a simple and amazing mechanism that offers infinite gear ratios.
Small History:

The Formula One (F1) sport is the most prestigious form of racing in the world. In 1993 The Williams FW15C for the testing purposes fitted with the completely different mechanism for the transmission of power from an engine to the wheels. This test model of Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT) technology was banned by F1 before hitting the race track. This technology is used as driver aid which reduces the driver’s efforts from shifting gears without any action by the driver and racing is not very challenging for completion.
Another big reason behind the ban was CVT powered car is quicker than manual gearbox and at the same time, they produces more noise. Japanese automobile manufacturing companies adopted this technology and implemented CVT in a very effective way and successfully presented joyful and effortless driving experiences to customers.
Also Read:
- Torque Converter Working, Principle, Main Parts and Application.
- Fluid Coupling – Main Parts, Principle , Working and Application
- How Automatic Transmission Works? – Best Explanation Ever
Main Parts of CVT
The basic CVT consists of
- Primary pulley
- Secondary pulley and
- Belt
1. Pulley and Sheave:
The gearbox is the only way of connecting the engine to the wheel. The vehicle does not require always the same power or constant power output, sometimes high torque-low speed and low torque-high speed gear ratios do their work. In the CVT system conical pulleys replace gear arrangement that is why it is also referred to as pulley transmission. The drive pulley or primary pulley is directly connected to the crankshaft of the engine. Whereas the driven pulley or secondary pulley is connected to the drive shaft (Means Output shaft –Differential-Wheel). Both pulleys have static and moveable sheaves, the combination of both static and moveable sheaves is called pulleys. Both pulleys have their own axle shaft and parallel to each other. Infinite gear ratios can be achieved by both pulleys driven by belt while pulleys diameter varies according to the movement of sheaves. The direction of contraction and expansion of pulleys at both ends are different. If the drive pulley expand then driven pulley contract at the same time and vice versa; let’s see how it works
At low speed:
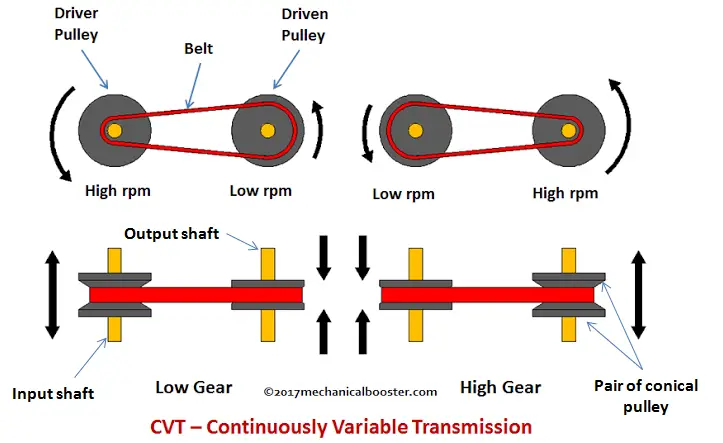
At the initial stage, the vehicle requires more torque (Doesn’t require speed) to move further, that is why a bigger gear is used as the first gear in the manual transmission. In the Continuously Variable Transmission system, the belt pushes the pulleys, and as soon as the crankshaft rotates the primary or driving pulley’s movable sheave moves away from the static sheave which makes the smaller diameter of the driving pulley. Due to the same movement of sheaves at the same time secondary or driven pulley becomes larger in diameter which leads to creating greater torque at the vehicle’s starting position.
At high speed or High Gear:
While accelerating, vehicle required high speed (Doesn’t required torque) for that driven pulley or secondary pulley diameter become smaller (smaller diameter more revolutions) as the moveable sheave moves away from the static sheave. Due to the same movement of sheaves at the same time, primary or driving pulley becomes bigger in diameter which creates gear ratio between them. One revolution at driving pulley is equal to four revolutions at the driven pulley.
How the sheave movement takes place?
Inside the conical sheave, it has cylindrical rollers. These rollers are subjected to undergo centrifugal force. Sheave pocket placed upon the rollers which take the movement of inside and outside as per roller gets centrifugal force. Whenever rpm increases or decreases these rollers push the pocket inside or outside.
2. Push Belt:
Push belt transfers the torque from driving pulley to the driven pulley. Two types of belts are used in continuously variable transmission. The V-Shape Kevlar rubber belt is used in the scooter which has more flexibility than the normal rubber belts. V-shape rubber can easily travel and pushes in-between the two pulleys. Steel belts are widely used in CVT; the construction of this belt is very unique, stronger and flexible than the V-shape belt. The complex steel belt has thin individual steel rings (Circular steel ring) and the whole bunch of small toothed steel elements that can easily travel and pushes the pulleys at any rpm range.
Working of Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT)
The manual and automatic transmission systems have complex working which depends upon gear shifting. There, two gears can achieve gear ratio, but in CVT two pulleys mechanism provides not only a single gear ratio but countless or infinite gear ratio. Both are connected by a push belt, one pulley (Primary) is connected with the engine and another (Secondary) pulley with a drive shaft. Each pulley attached with a moveable sheave which causes expansion and contraction of the pulleys at both ends. As the engine turns the primary pulley and secondary pulley diameter size gets changed due to moving sheaves of both pulleys. If one pulley’s size is decreased, at the same time the second pulley’s size is increased and vice versa. The size variation of pulleys means diameters also varies which creates the continuous gear ratios. In manual gearbox input and output gear teeth decides the ratios, but here variation in diameter decides the ratios.
Also Read:
- How Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) Works?
- Manual Vs Automatic Transmission
- Different Types of Engine
Advantages:
- Lightweight, compact, and easy to handle.
- Smooth-shifting and it offers a smooth ride, No up and downshifting problem, and jerking can be eliminated.
- Reduces the fuel consumption (up to 6-10 percentage) and no power loss due to no gear arrangement.
- Better fuel economy and efficiency.
- Quick and better acceleration.
Disadvantages:
- Very expensive and if any damage occurs it needed a costly repair.
- It cannot transmit more torque and cannot withstand high horsepower because it is a belt-driven system.
- Not long-lasting.
- Noise from the CVT system is more during acceleration as compared to usual transmission
Applications:
Continuously Variable Transmission is used in automotive vehicles as the advanced transmission system
- Examples: Scooters and Cars, Honda Activa.
- Best CVT Cars available in India are Honda Amaze VX , Honda Civic, Honda City SV, Maruti Suzuki Baleno, Nissan Micra XL , Toyota Corolla Altis.
